PEM Fuel Cells Theory And Practice
BlogWith great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to PEM Fuel Cells: Theory and Practice. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.



Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) are a type of electrochemical cell that generates electricity through the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen. They are a promising technology for clean and efficient power generation, with applications in transportation, stationary power, and portable devices.
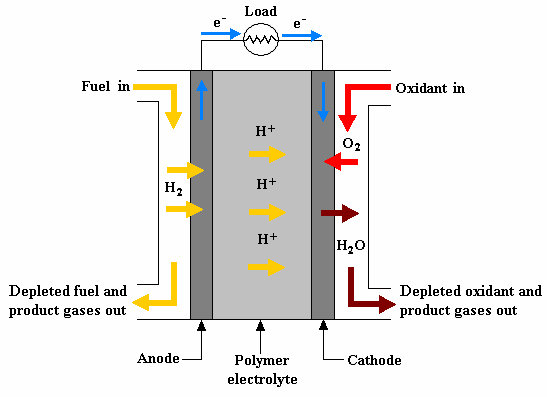
PEMFCs operate on the principle of electrochemistry. Hydrogen gas is fed into the anode of the cell, where it is oxidized to form protons (H+) and electrons. The electrons are conducted through an external circuit, generating an electrical current. The protons pass through the proton exchange membrane (PEM) to the cathode, where they react with oxygen to form water.

The PEM is a key component of the fuel cell. It allows protons to pass through while blocking electrons, creating a separation between the anode and cathode reactions. The PEM is typically made of a polymer such as Nafion.

Research and development efforts are ongoing to address these challenges. Advances in materials science, manufacturing techniques, and system design are expected to improve the performance, durability, and cost of PEMFCs.

PEMFCs are a promising technology for clean and efficient power generation. They have a wide range of potential applications, but they face several challenges. Ongoing research and development efforts are expected to overcome these challenges and enable the widespread adoption of PEMFCs.










Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into PEM Fuel Cells: Theory and Practice. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
